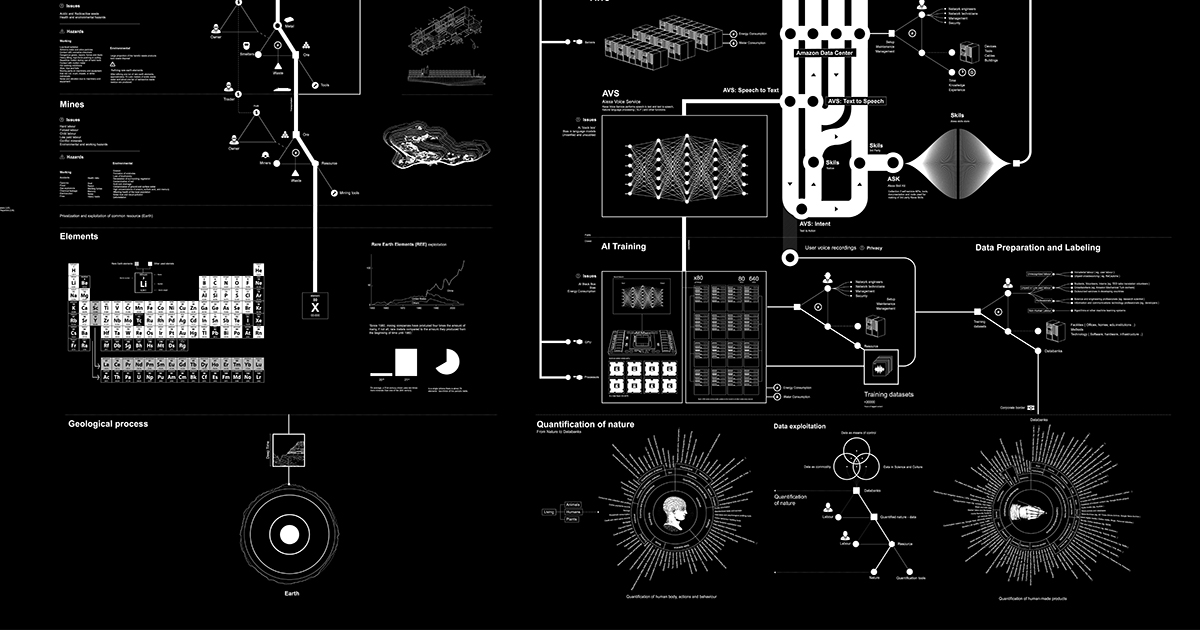
On Making in the Digital Humanities fills a gap in our understanding of digital humanities projects and craft by exploring the processes of making as much as the products that arise from it. The volume draws focus to the interwoven layers of human and technological textures that constitute digital humanities scholarship.
On Making in the Digital Humanities is finally out from UCL Press. The book honours the work of John Bradley and those in the digital humanities who share their scholarship through projects. Stéfan Sinclair and I first started work on it years ago and were soon joined by Juliane Nyhan and later Alexandra Ortolja-Baird. It is a pleasure to see it finished.
I co-wrote the Introduction with Nyhan and wrote a final chapter on “If Voyant then Spyral: Remembering Stéfan Sinclair: A discourse on practice in the digital humanities.” Stéfan passed during the editing of this.