Mikhail Epstein Hyper in 20th Century Culture: The Dialectics of Transition From Modernism to Postmodernism (Postmodern Culture 6:2, 1996) explores “the intricate relationship of Modernism and Postmodernism as the two complementary aspects of one cultural paradigm which can be designated by the notion ‘hyper’ and which in the subsequent analysis will fall into the two connected categories, those of ‘super’ and ‘pseudo.'” (para 7) Epstein plays with “hyper” as a prefix meaning that excess that goes beyond a limit then reflecting back on itself. Modernist revolutions overturn the inherited forms in a search for the “super” which in their excess zeal pass a limit becoming simulations of themselves or “pseudo”. The hyper encloses both the modernist search for the super truth and the postmodernist reaction to the simulations of modernity. The postmodern play on the excess depends on the modernist move for matter to the point where it serves to heighten (another meaning of hyper) the super-modern. Super and pseudo thus become intertwined in the ironic hyper.
In the final analysis, every “super” phenomenon sooner or later reveals its own reverse side, its “pseudo.” Such is the peculiarly postmodernist dialectics of “hyper,” distinct from both Hegelian dialectics of comprehensive synthesis and Leftist dialectics of pure negation. It is the ironic dialectics of intensification-simulation, of “super” turned into “pseudo.” (para 60)
Epstein looks at different spheres where this hyper-unfolding takes place using the word “hyper-texuality” in a different sense than how it is usually used for electronic literature. For Epstein hypertextuality describes a parallel process that happened in Russia and in the West where first modernist literary movements (Russian Formalism and Anglo-American New Criticism) stripped away the historical, authorial, and biographical to understand the pure “litterariness” of literature. The purification of literature left only the text as something “wholly depednent on and even engendered by criticism.” (para 21) “Postmodernism emerged no sooner than the reality of text itself was understood as an illusionary projection of a critic’s semiotic power or, more pluralistically, any reader’s interpretative power (‘dissemination of meanings’).” (para 25)
Epstein quotes Baudrillard about the net of mass communication replacing reality with a hyperreality, but doesn’t explore how the hyper in his sense is connected to the excess of networked information. It is in another essay, “The Paradox of Acceleration” that we see a clue,
Each singular fact becomes history the moment it appears, preserved in audio, visual, and textual images. It is recorded on tape, photographed, stored in the memory of a computer. It would be more accurate to say that each fact is generated in the form of history.
…
Ultimately, inscription of the fact precedes the occurrence of the fact, prescribing the forms in which it will be recorded, represented, and reflected.” (p. 179)
The ironic tension of the modern and postmodern is magnified by the hyper-excess of automated inscription. The excess of information is deadening us to the human in history as an unfolding. We are in a baroque phase where the only thing valued is the hyper-excess itself. Excess of archiving, excess theory, excess of reference, excess of quotation, excess of material, excess of publication, excess of criticism, excess of attention … but no time.
What next? Will we see the burning of books or a “simple thinking” movement? How do people react to an oppressive excess?
The essay in PMC is excerpted from an essay, “The Dialectics of Hyper: From Modernism to Postmodernism.” in Russian Postmodernism; New Perspectives on Post-Soviet Culture. Ed. M. Epstein, A. Genis, and S. Vladiv-Glover. New York: Berghahn Books, 1999. p. 3-30.
The essay on acceleration is, “The Paradox of Acceleration.” also in Russian Postmodernism. p. 177-181.
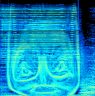 bastwood.com has a good page on images found in sound starting with the demon face in Aphex Twin’s “Windowlicker”. It turns out the demon is really an inverted version of the Twin himself. The site goes on to discuss how to find such images and how to create sound from images using common software.
bastwood.com has a good page on images found in sound starting with the demon face in Aphex Twin’s “Windowlicker”. It turns out the demon is really an inverted version of the Twin himself. The site goes on to discuss how to find such images and how to create sound from images using common software. This weekend I participated in an
This weekend I participated in an